KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT
What Is Knee Osteoarthritis?
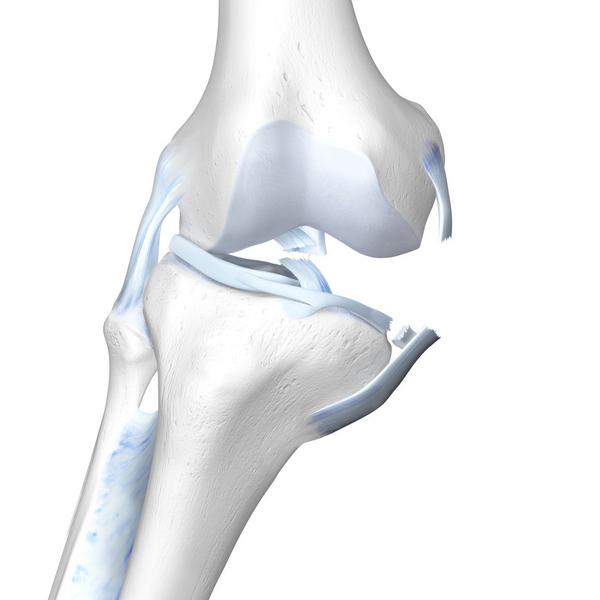
The knee joint is a complex structure consisting of bone, ligaments and cartilage. It facilitates movement and allows us to walk, run and jump. Long term wear and tear of the joint leads to the development of knee osteoarthritis.
Knee Osteoarthritis refers to the condition where there is inflammation due to arthritis. It is usually accompanied by pain and swelling.

WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GONARTHROSIS AND KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS?
The degeneration of the knee joint, due to this long term wear and tear, is often referred to as gonarthrosis. Knee Gonarthrosis is a non-inflammatory condition related to aging population.
In mild cases, a patient experiences episodic pain after long periods of inactivity, like a long day seated at work. Gonarthrosis is fairly common in elderly adults but is not exclusively a disease of old age.
In chronic cases, the entire knee joint can be compromised and in the worst-case scenario, a knee replacement may become necessary.
CAUSES & TYPES OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS
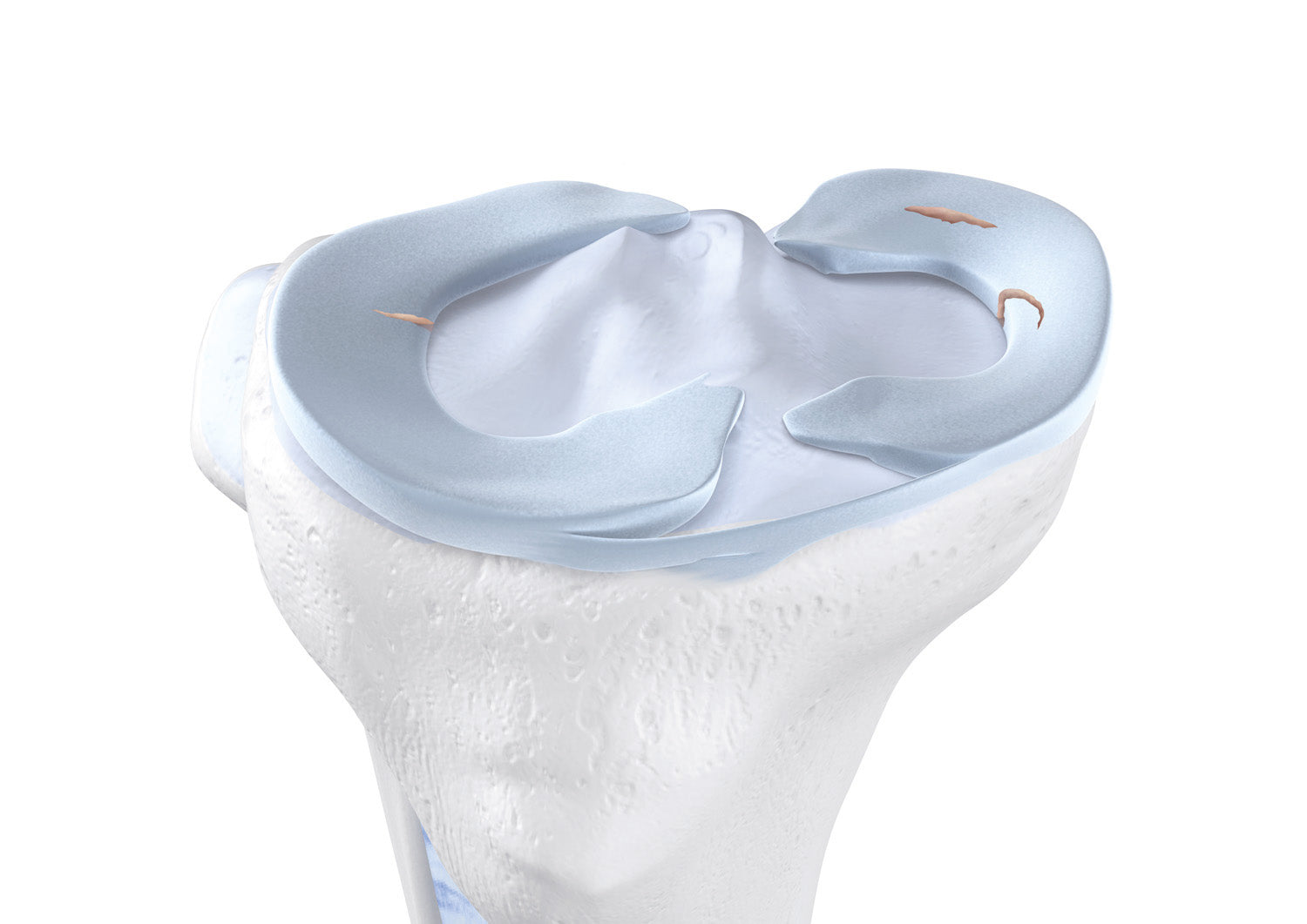
Knee Osteoarthritis (medically known as Gonarthrosis) is described as the damage to the cartilage inside the knee joint. The damage is irreversible and can significantly restrict one’s mobility.
Based on the root of the disease, there are two distinct types:
- Primary (Internal) and
- Secondary (External)
Primary Knee Osteoarthritis is rather mysterious. The true root of the disease is unknown; however, scientists suspect that pre-existing conditions and a hereditary disposition could be the trigger. Not all carriers of the gene manifest symptoms. Lifestyle choices, including lack of exercise and obesity, are also suspected triggers.
Secondary Knee Osteoarthritis is easier to diagnose and has a clear origin. Risk factors for developing secondary gonarthrosis include:
- Sporting accidents or physical trauma to the knee.
- High-intensity physical activity, which labourers and tilers experience.
- Long periods of inactivity like in long hours at a desk job.
OSTEOARTHRITIS KNEE SYMPTOMS
Osteoarthritis in the knee joint is caused due to a defect of the cartilage covering inside the knee joint. Cartilage acts as a shock absorber and allows us to smoothly bend and stretch the knee.
Some of the common symptoms of osteoarthritis in the knee include:
- Knee pain when climbing stairs and walking on uneven terrain
- Increased discomfort when carrying heavy objects
- Episodic pain that subsides
- Pain behind the kneecap after long periods of sitting
- Increased sensitivity in wet and cold weather
- Crunching noises when the affected knee moves
Mild Osteoarthritis Knee Symptoms
- Even in mild cases, the underlying condition still exists. Immediate treatment is highly recommended to stop the progression of the disease. The earlier the diagnosis, the better the prognosis!
- If left untreated, the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage reduce the joint gap. Long term wear and tear of the buffer causes the upper and lower leg bones to grind against each other.
- The patient consequently experiences pain and discomfort. The skin around the knee then begins to turn red and there may be swelling present.
Chronic Osteoarthritis Knee Symptoms
- In chronic cases, bony tips, called osteophytes, begin to grow on the edge of the knee joint.
- As a result of the knee becoming stiff and immobile, the patient experiences sharp pain and severely restricted mobility.
- The joint is compromised and requires external support to avoid buckling. In the worst-case scenario, a patient might need a complete knee replacement.
DIAGNOSING OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE

Effective diagnosis begins with a comprehensive physical examination by a doctor. The physician examines the knee joint and the surrounding area to check for pressure-sensitive and swollen areas. A complete history is also taken to check for the possibility of pain from bad proprioception.
Osteoarthritis Knee X-Ray
- The physician conducts a joint mobility test to study the extent of stiffness in the knee.
- Sophisticated technology, like X-ray imaging, allows the physician to check the distance between the articular surfaces of the knee joint (the joint gap).
- Ultrasound and MRI’s can also be used to easily identify damaged muscles, cartilage and tendons.
KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS (GONARTHROSIS) TREATMENT
Knee Osteoarthritis or Gonarthrosis is irreversible and the best treatment course involves managing the pain as the disease progresses. A good guideline to follow is:
Lifestyle Changes - A Multi-Disciplinary Approach
- Lifestyle changes in the early stages of the condition can help slow the progression.
- Avoiding stressful activities, like intensive manual work and walking on uneven terrain, is a proven effective measure a patient can take in their daily life.
- Healthy nutrition and weight loss significantly help to reduce the strain on our knees and is also beneficial in managing gonarthrosis.
Rehabilitation And Physiotherapy Exercises For Osteoarthritis Of The Knee
- Regulated physiotherapy helps with targeted muscle training and is a proven effective treatment path.
- The exercises can help promote reorganization of the muscles and are the most effective option to curb the disease.
- Encouraging healthy proprioception and strengthening of the muscles helps prevent long term degeneration and can slow the progression of gonarthrosis.
Prescribed Painkillers
- Medication, such as Ibuprofen or Panadol, can be used to help alleviate pain and discomfort in patients suffering from gonarthritis.
- Pain, however, is a crucial indicator of the injury. Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition.
- Long term use of painkillers has side-effects and can be counterproductive.
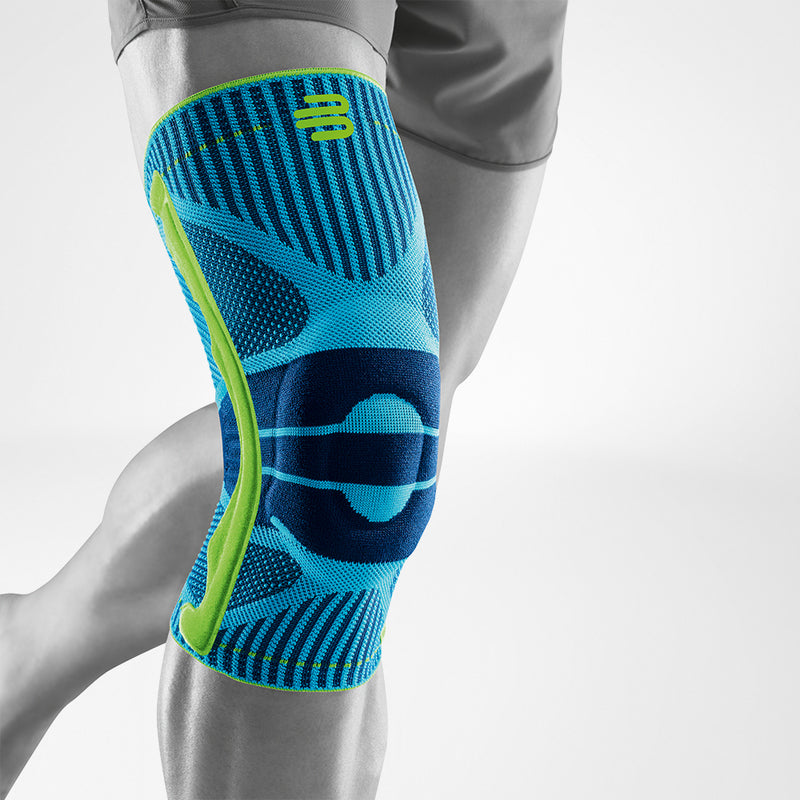
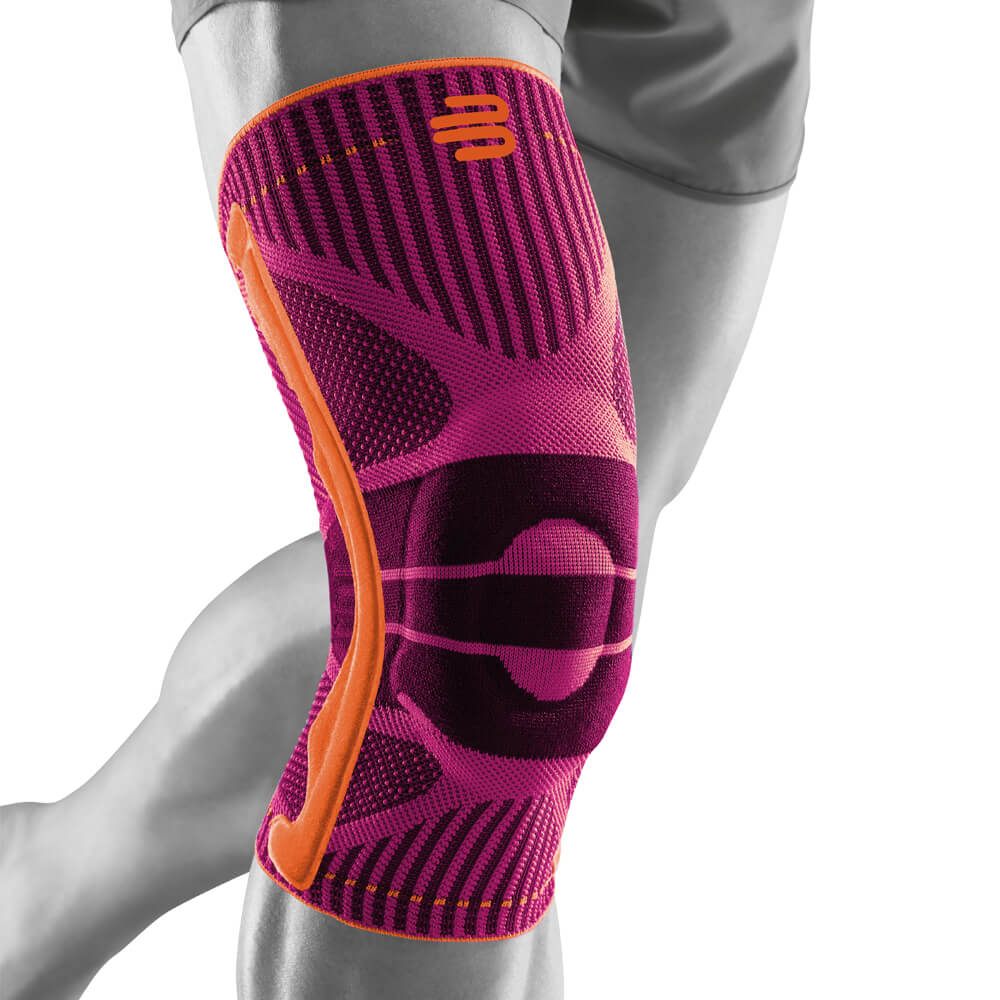
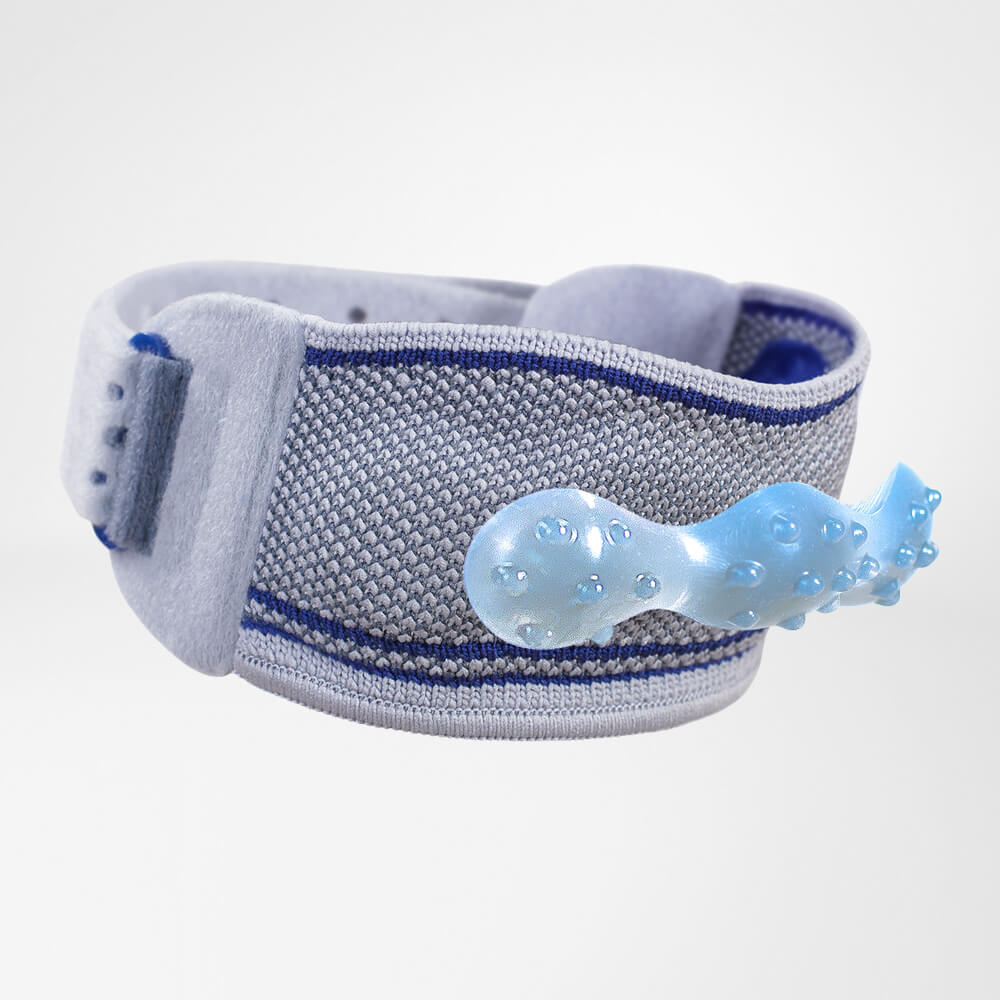
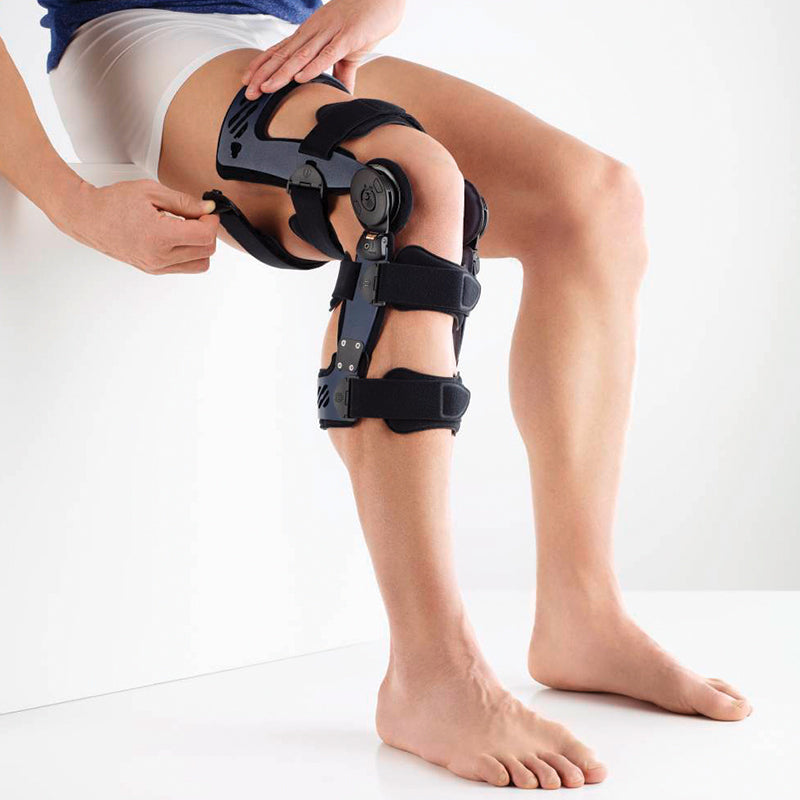
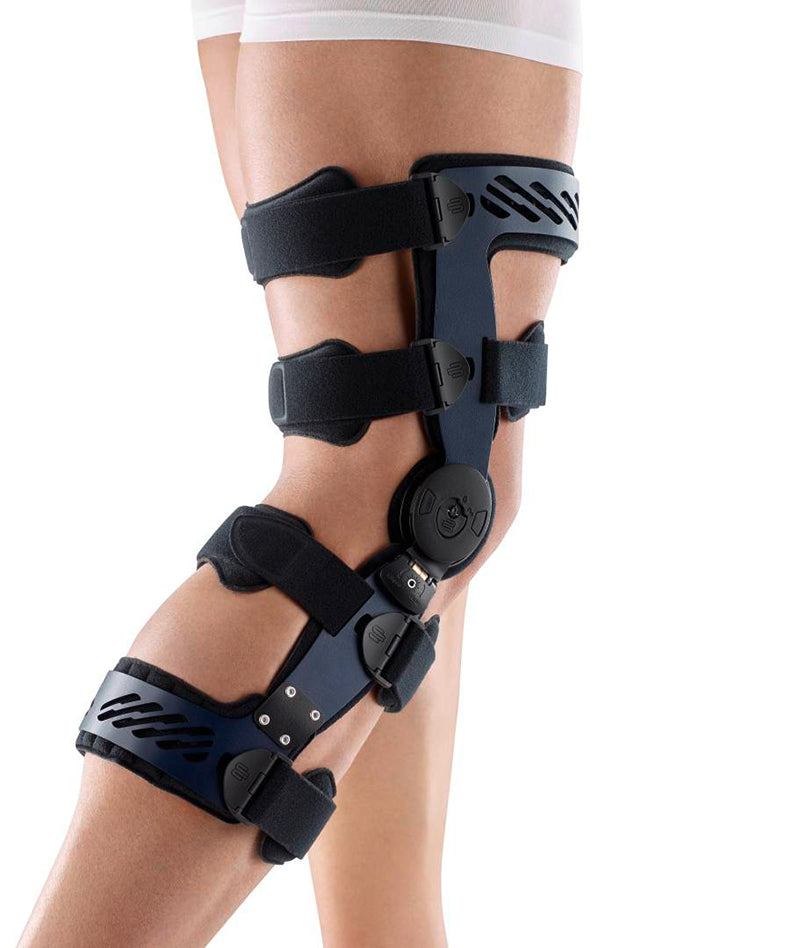
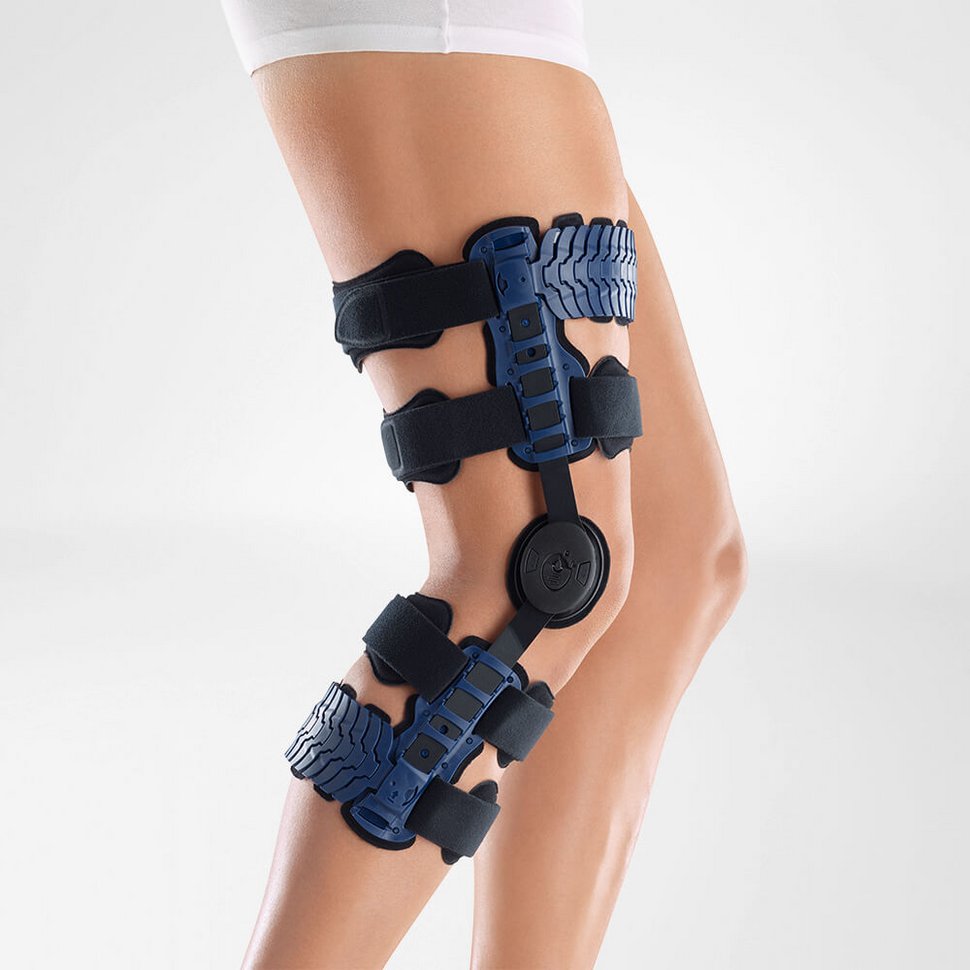
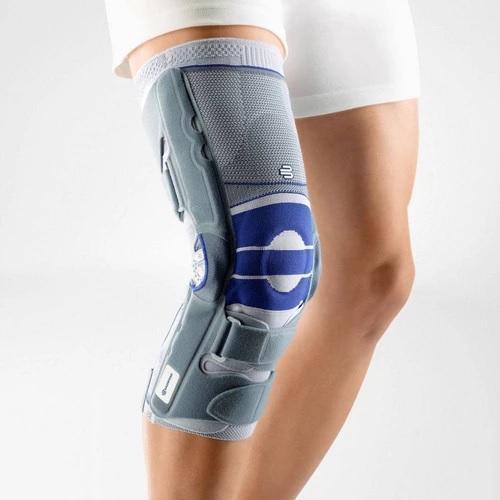
Medical Knee Braces For Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
- It is highly recommended that ample support is provided to the knee joint through the use of a medical knee brace.
- The targeted compression that braces provide help to boost circulation and reduce the possibility of effusions and edema.
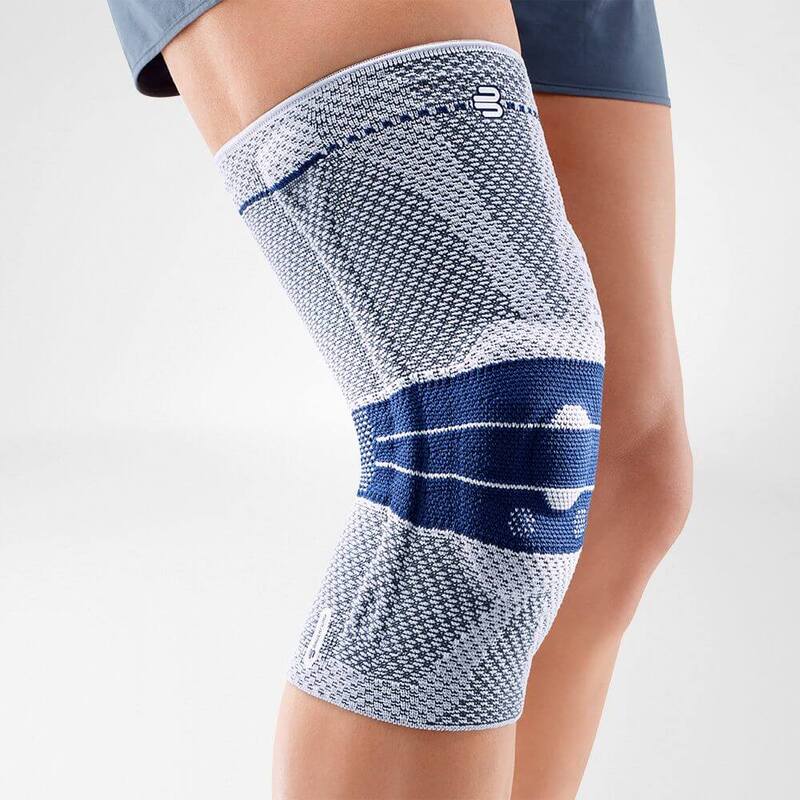
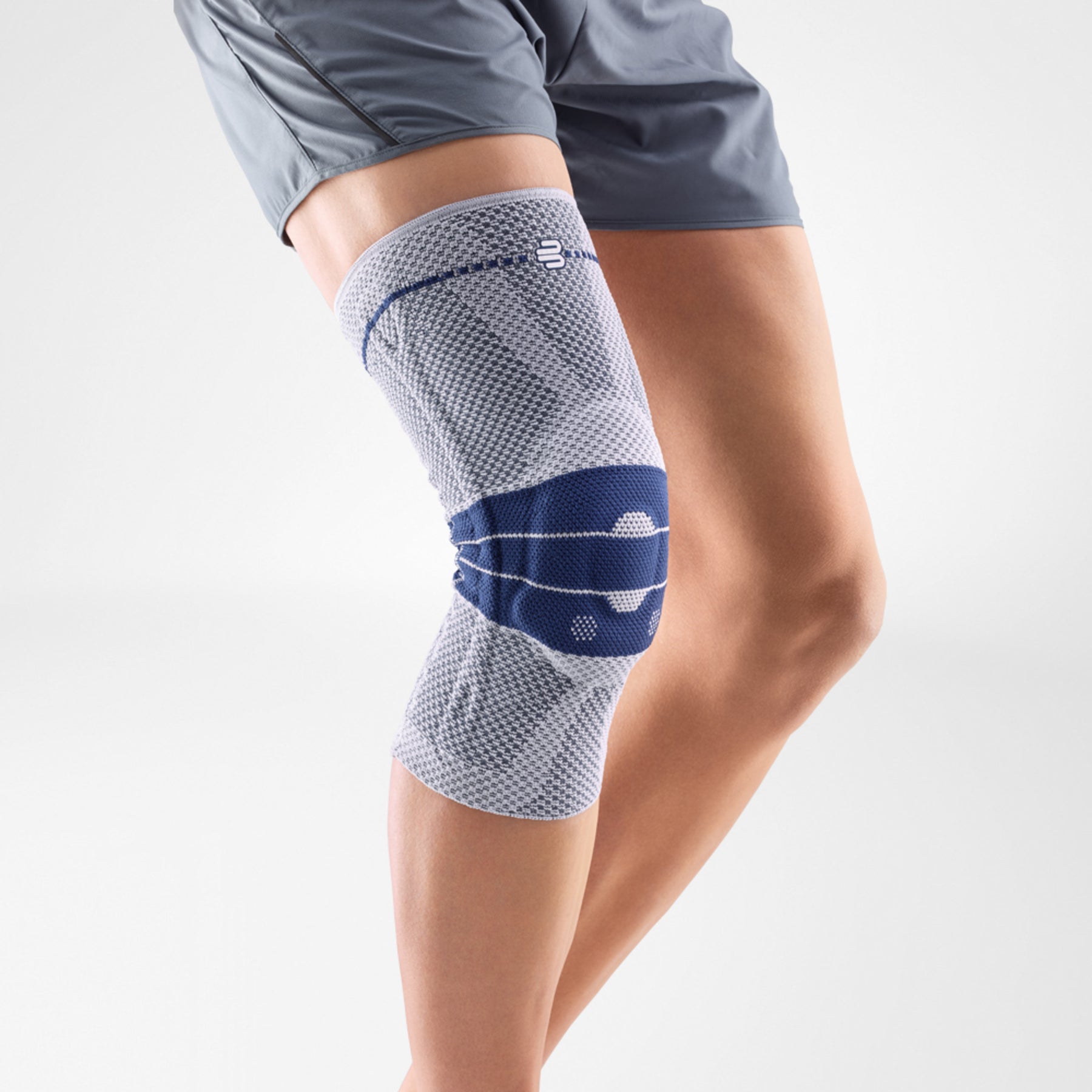
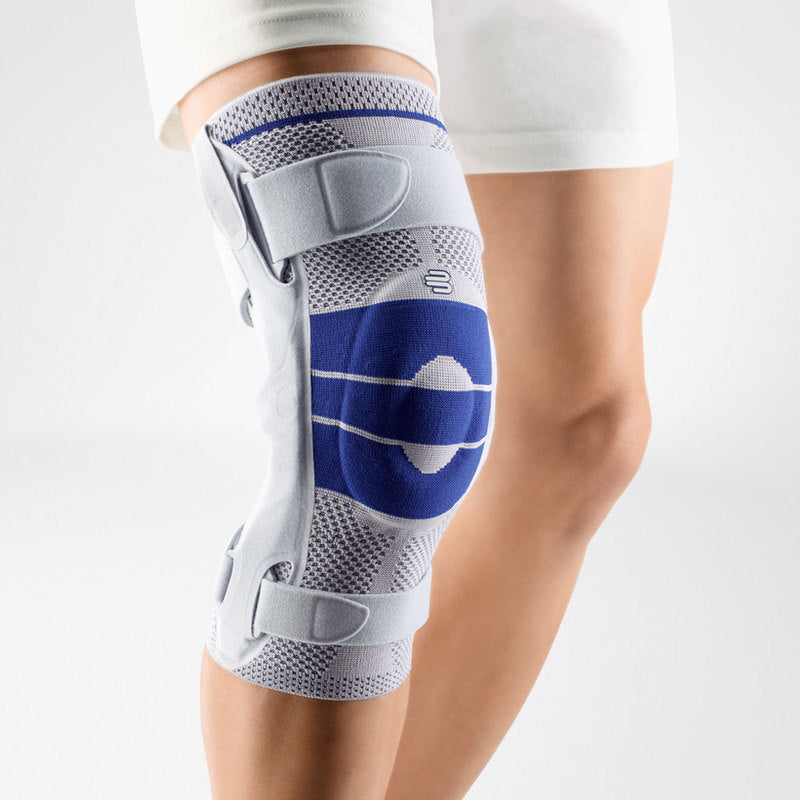
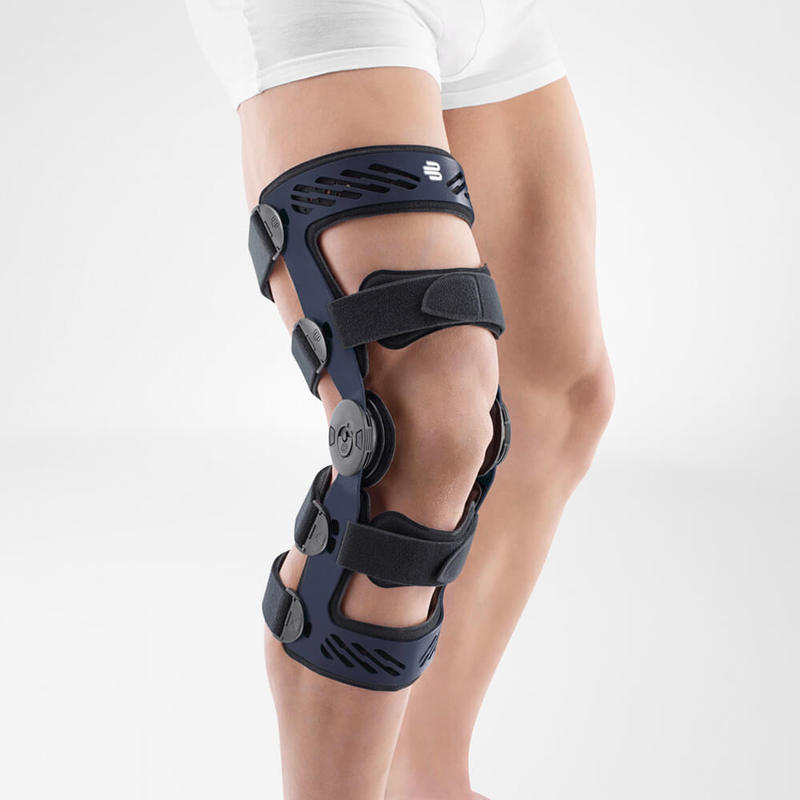
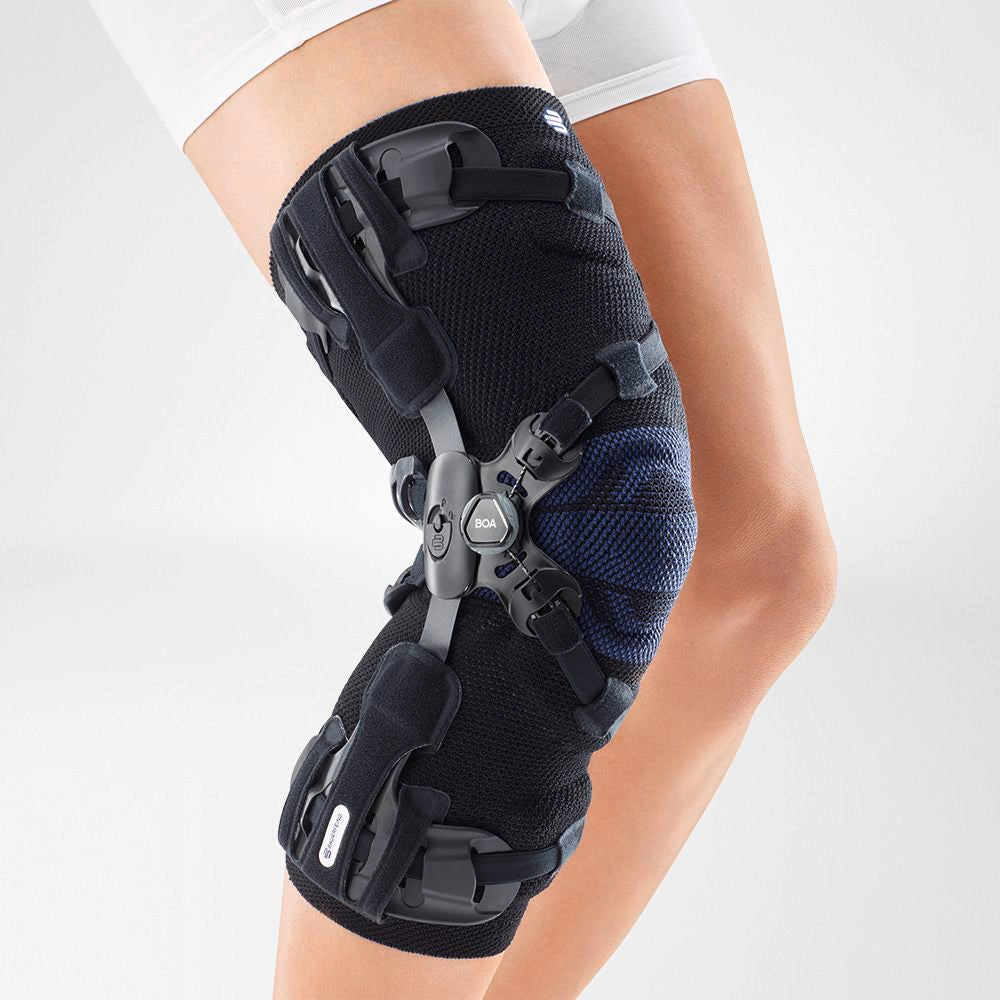
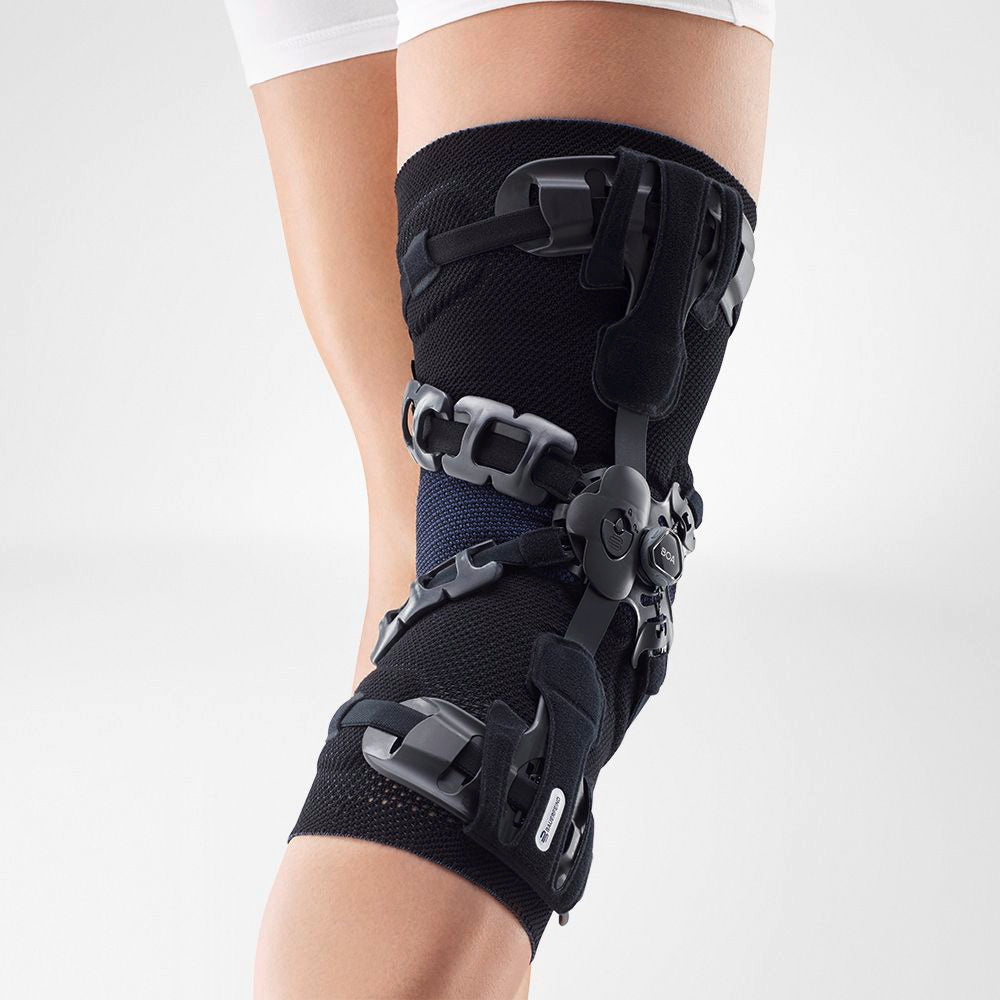
- Wearing a Bauerfeind knee brace, like the GenuTrain OA or SecuTec OA, can minimise chances of injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression. These benefits are not found in simple neoprene sleeves and braces.
Surgical Intervention
- Operative surgery is considered only in extreme cases where symptoms are persistent, and all conservative treatments have been exhausted.
- In chronic conditions of bone growth, surgery might be needed to restore mobility.
- In the worst-case scenario, a knee replacement could be a final resort if all other measures fail to provide relief.
HOW TO FIX OSTEOARTHRITIS IN THE KNEE USING ORTHOSIS?

Exercise and restrengthening is a tried and tested remedy in treating gonarthrosis (knee osteoarthritis) pain.
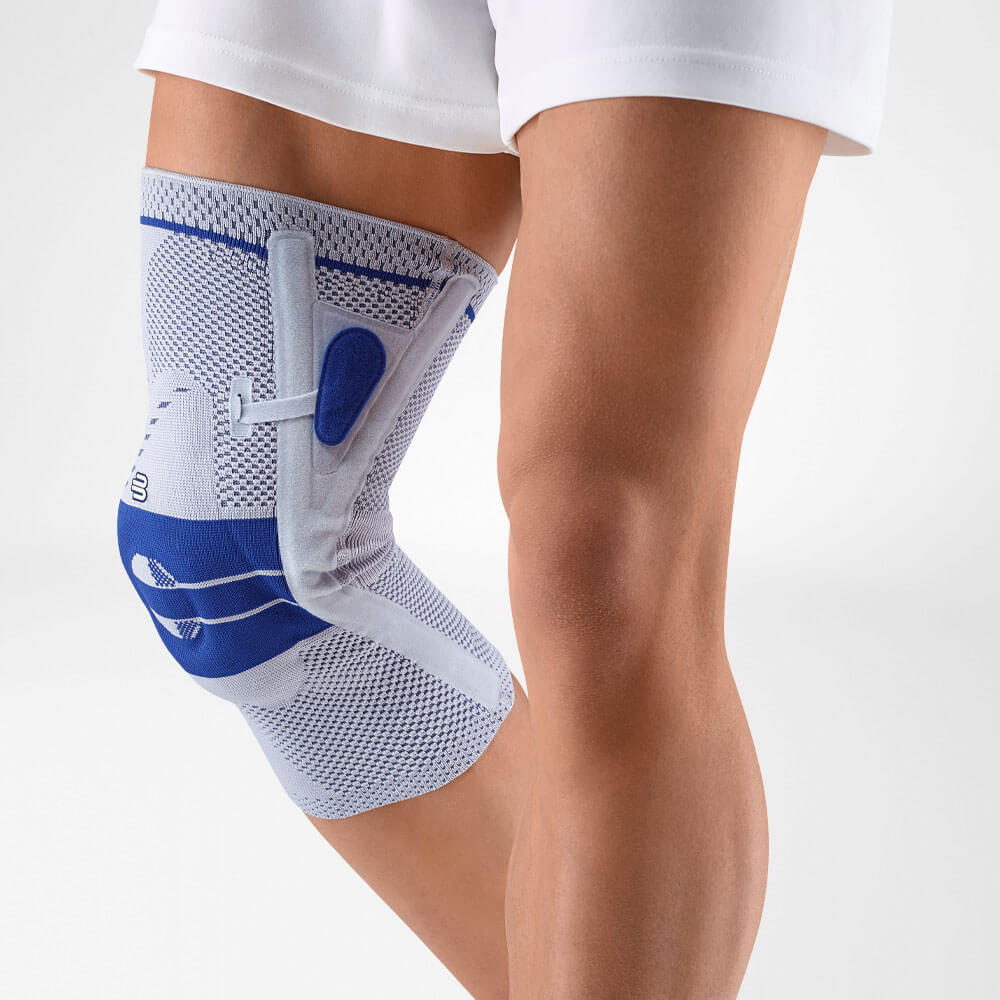
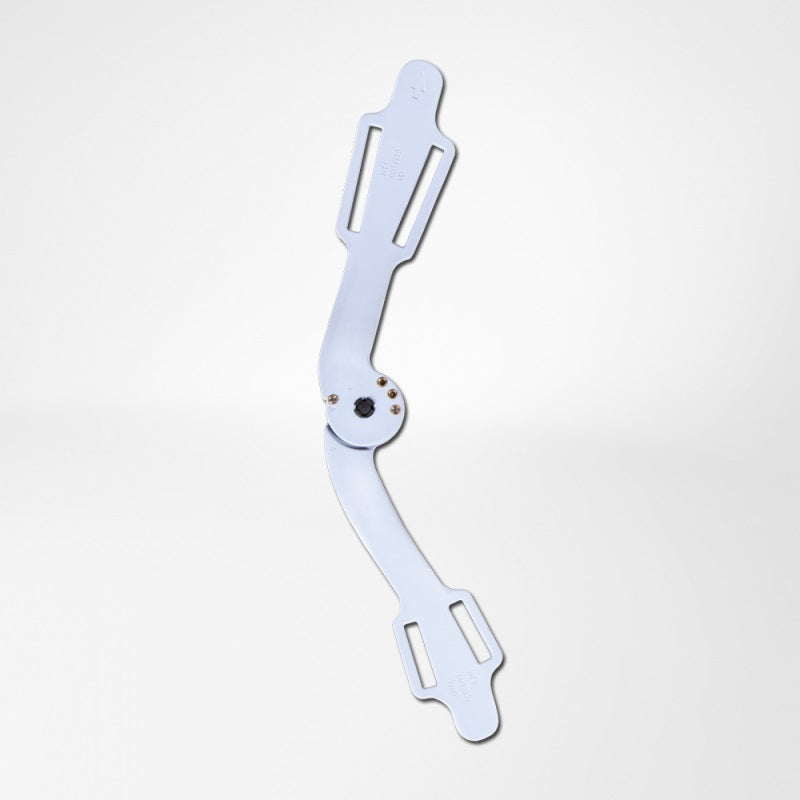
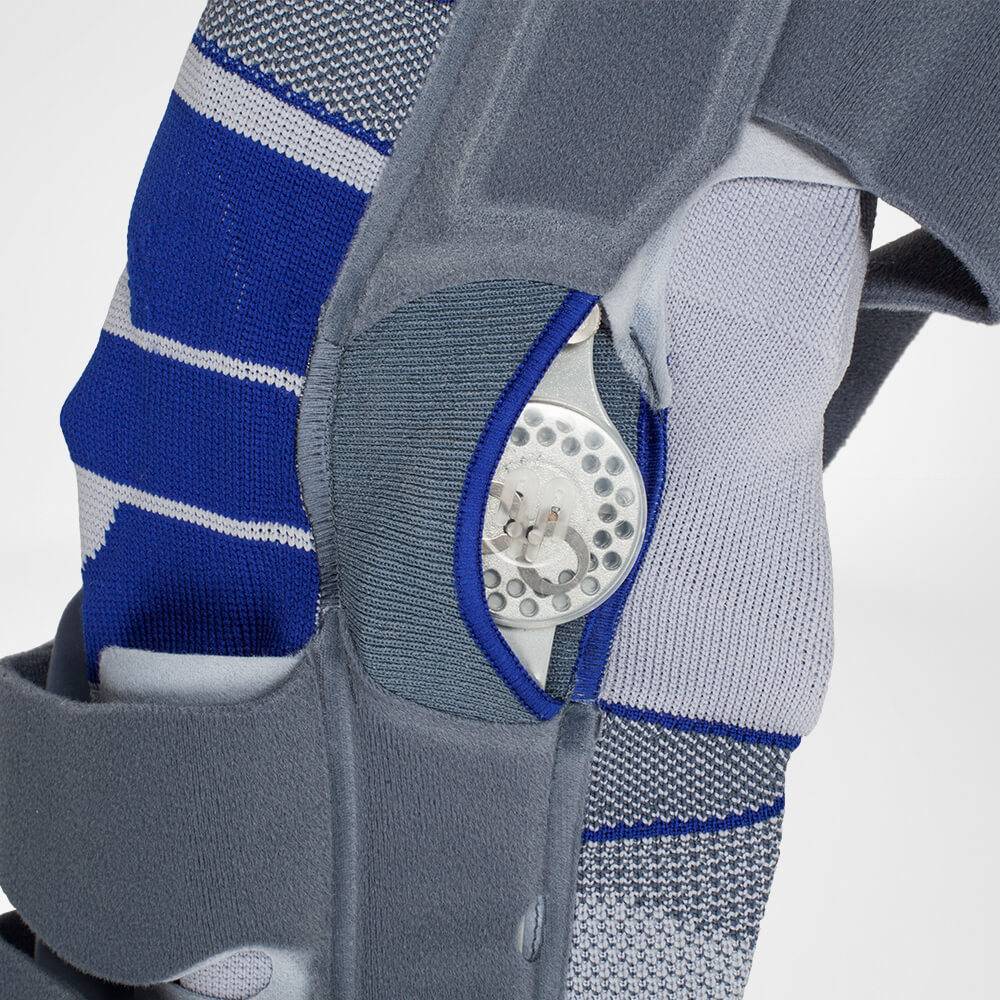
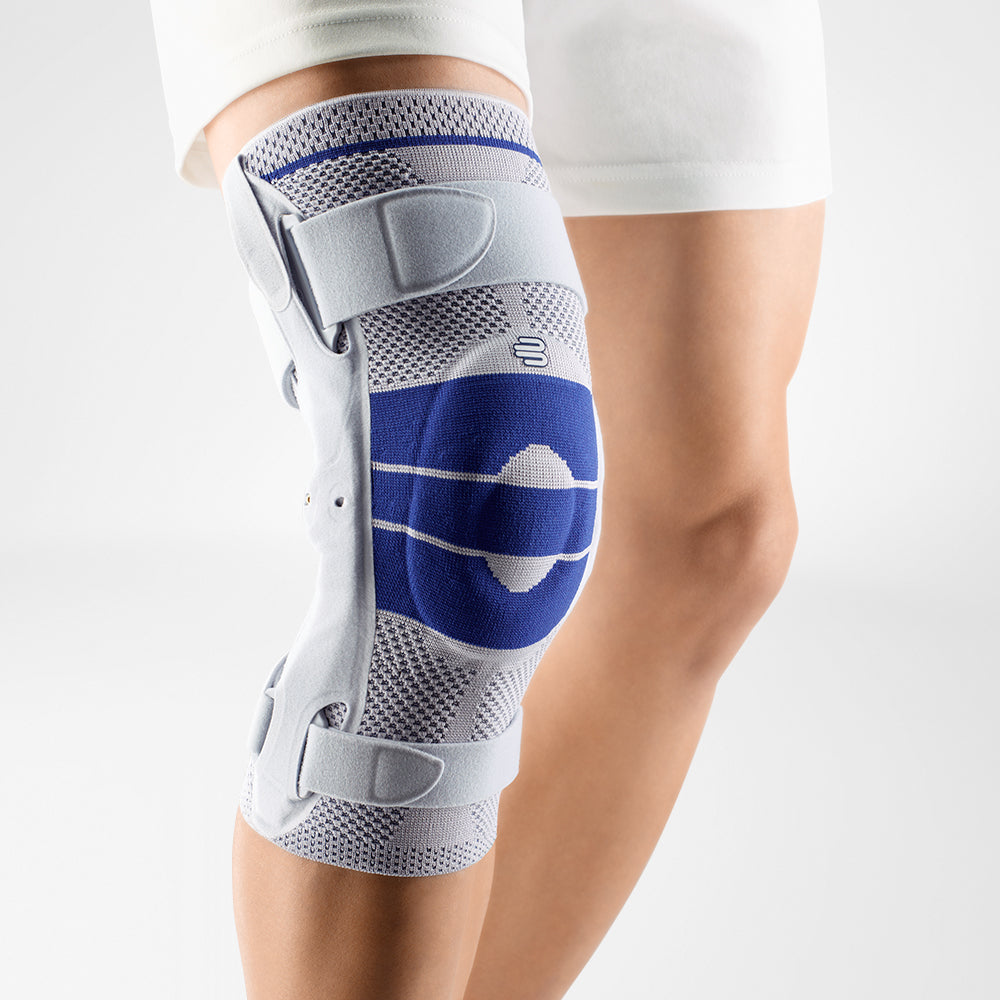
- A medical knee brace, like Bauerfeind’s GenuTrain OA, is instrumental in a speedy recovery as it provides the knee with support and stability.
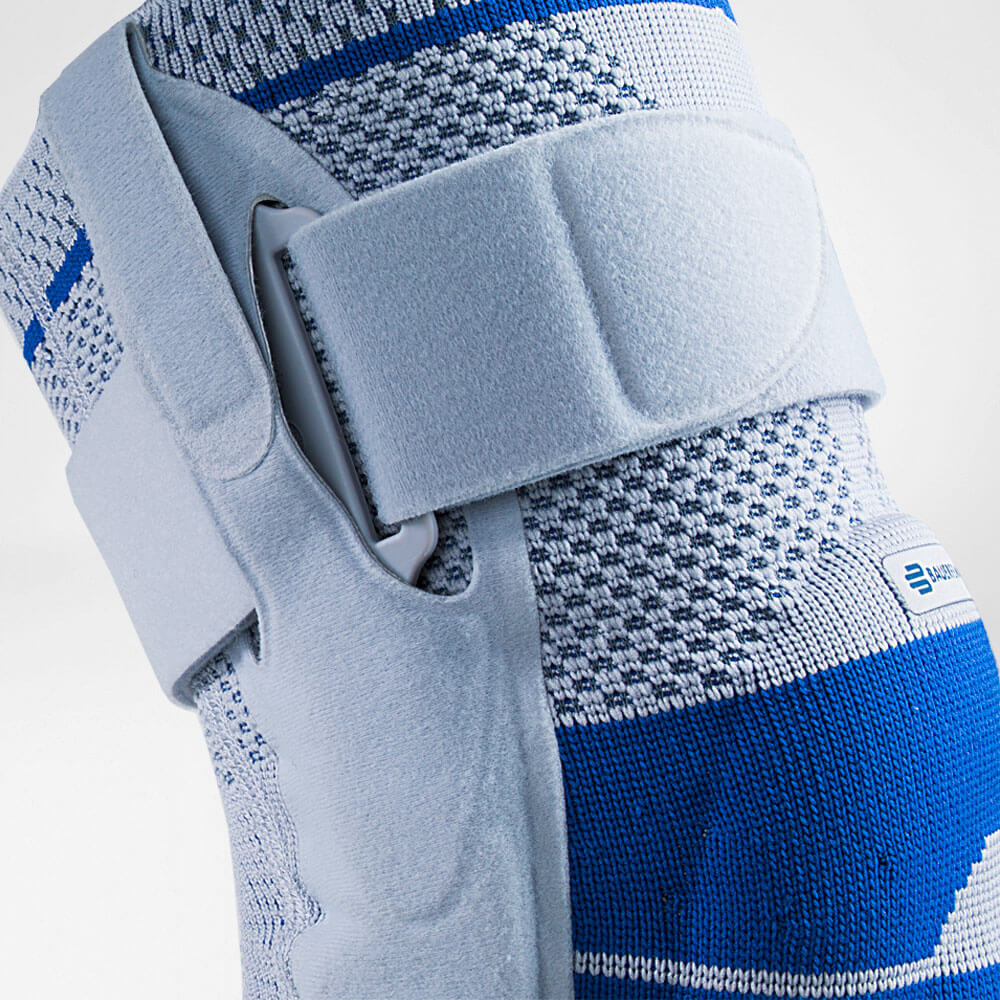
- Developed specifically for knee osteoarthritis, the GenuTrain OA knee brace features an unloading and stabilising system which noticeably reduces the pain experienced within the knee joint.
- With the addition of the Boa closure system, the patient can easily adjust the amount of unloading required to adapt to a wide range of daily activities, including walking or hiking.